A tooth infection can be highly uncomfortable and, if left untreated, can lead to more serious oral health issues. In some instances, the disease can spread deep into the inner recesses of the tooth, reaching the pulp, the tooth’s soft tissue. The result could be severe pain and possibly the infection of a tooth. How do you know when a simple toothache is more than a minor inconvenience? Knowing the signs and treatments puts you in the best position to make decisions about your oral health.
A root canal is generally a potential life-saving treatment for an ailing tooth that would otherwise need to be removed from the mouth. It is a common myth that root canal treatments are painful. The truth, however, is that modern dentistry has made it comfortable and quite efficient. So, let’s see what a root canal is and why it is performed.
What is a Root Canal and Why is It Needed?
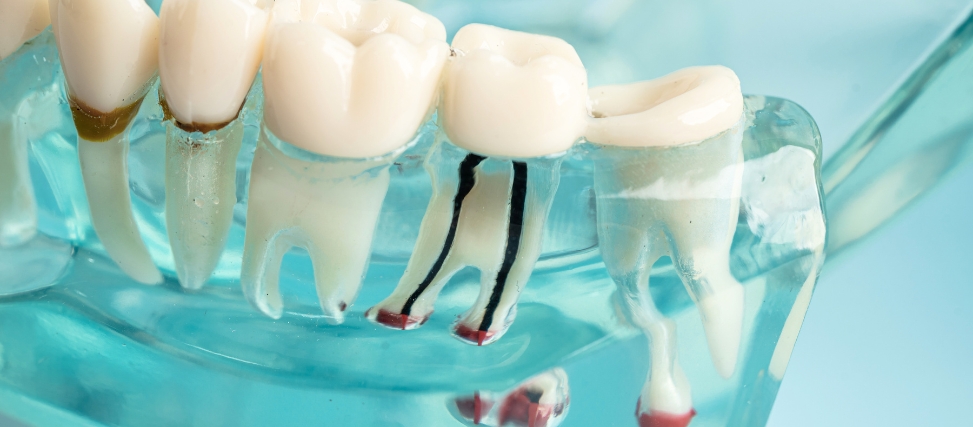
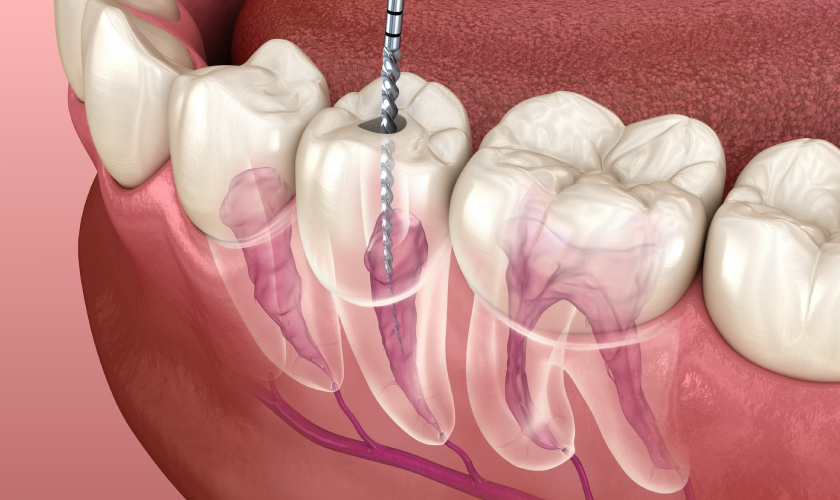
A root canal is a dental treatment performed by a dentist or an endodontist to remove infected or damaged tissue from within the tooth. When bacteria enter the tooth through a crack, chip, or deep cavity, an infection can develop in the pulp, which contains the nerves and blood vessels. Such infection reaches the pulp, causing pain, swelling, and other symptoms.
A root canal in Colleyville, TX, helps remove the infection, saving the tooth and restoring it to health. It involves the tooth’s inner pulp, which can be damaged by infection or injury. The manifestations of this complication include continuous toothache, tooth sensitivity, especially to hot and cold, swelling around the tooth, and, in some cases, an abscess. If left unattended, the infection will spread, leading to serious complications, including tooth loss.
Does Root Canal Treatment Hurt?
Root canal treatment is usually no more painful than getting a filling. Actually, most people find pain relief with the removal of infected tissue. Local anesthesia will numb the area to ensure comfort during the procedure.
The days following the procedure may be associated with some discomfort, which is usually well-tolerated with over-the-counter pain relievers. Inflammation in the surrounding tissues generally causes discomfort, but this usually subsides within days.
When to Seek Treatment for an Infected Tooth?
If you have any persistent toothache or sensitivity, don’t wait until later to seek treatment. Early root canal treatment increases the likelihood of tooth salvage. If left untreated, the infected tooth can lead to more serious problems, including abscesses and bone loss.
In many cases, a root canal is the most viable way to save a tooth. It is a widely used procedure with a high success rate, enabling you to retain your natural smile for many years to come.
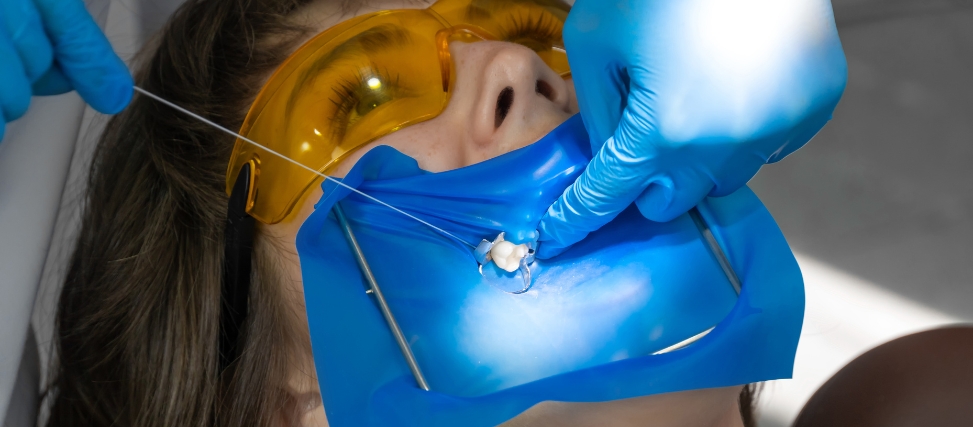
Root Canal Treatment Steps
The steps involved in root canal treatment are simple and effective for saving your tooth and relieving discomfort. Here’s a breakdown of the key steps involved in the procedure:
- Anesthesia: The dentist begins by numbing the area around the tooth to ensure you’re comfortable throughout the procedure.
- Accessing the Tooth: The dentist creates a small opening in the tooth to reach the infected pulp inside.
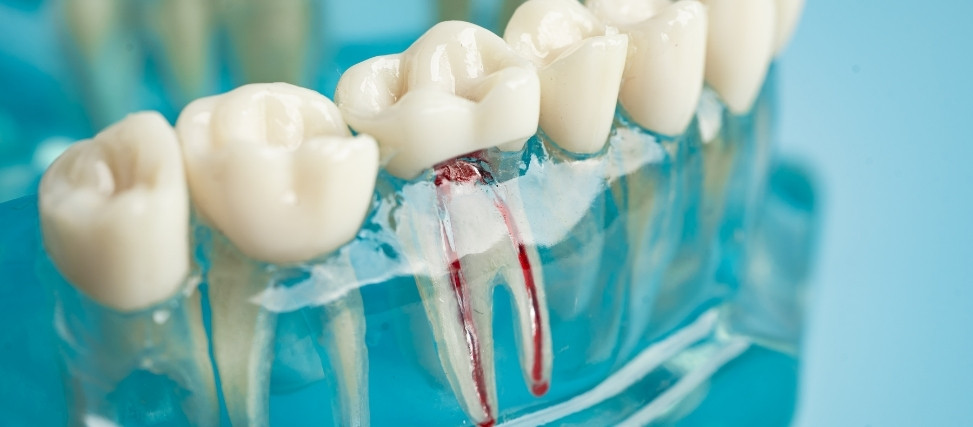
- Removing the Infected Pulp: The diseased tissue is carefully removed from the tooth, eliminating the source of pain and infection.
- Cleaning the Tooth: The inside of the tooth is thoroughly cleaned to remove any remaining bacteria and ensure a healthy environment for healing.
- Sealing the Tooth: A special material is used to seal the tooth and prevent future infections.
- Crown Placement: In most cases, a crown is placed over the tooth to restore its structure and protect it from further damage.
Root Canal Recovery Time
Recovery after a root canal is usually quite quick. Your tooth may be sensitive for a while, but this should settle down as it heals. Most people can go back to their normal activities straight after the procedure.
Follow the aftercare instructions given to you by the dentist. This may include avoiding chewing on the treated tooth until it’s fully healed and practicing good oral hygiene.
If these symptoms are severe and do not regress after a few days, it is essential to call your dentist to rule out complications.
Act Now to Save Your Tooth
If you think your tooth might be infected, it is essential to see a dentist or an endodontist right away. A root canal can relieve the pain and prevent further complications, thus saving your tooth and your smile. Don’t wait until the infection worsens; make an appointment today.
At Serene Dental of Colleyville, we are committed to providing the best care for your dental needs. Our team of professionals will ensure you are as comfortable and well-informed about your treatment as possible. If you think your teeth may be in pain or infected, let us know so we can set up a consultation. Book your appointment with us today and take the first step toward a pain-free smile.
FAQs
- What are the signs that I need a root canal?
If you are feeling persistent tooth pain, especially when chewing or applying pressure, it could be a sign that you need a root canal. Other warning signs include heightened sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures, even after the source of heat or cold is removed. Swelling or tenderness around the tooth or gums is another indicator of an infection that requires immediate attention. - How long does root canal recovery take?
Most people can expect a relatively quick recovery after a root canal. You may feel mild discomfort or sensitivity for a few days following the procedure. However, this is normal and can be managed with over-the-counter pain relief. Following your dentist’s aftercare instructions will help ensure a smooth and speedy recovery. - Can I eat after a root canal?
It’s best to avoid chewing on the treated tooth until the anesthesia fully wears off and the tooth is restored, usually with a crown. This helps prevent any accidental damage to the tooth or the surrounding tissues. Your dentist will advise you on when it’s safe to resume eating normally, but you’ll typically be able to eat soft foods soon after the procedure. - What happens if I ignore the need for a root canal?
Ignoring the need for a root canal can lead to the infection spreading, causing more severe pain, swelling, and even the formation of an abscess. Infected teeth can ultimately become so damaged that extraction is the only option. It’s essential to seek treatment as soon as you notice symptoms to save your tooth and prevent further complications. - How can I prevent needing a root canal?
Maintaining good oral hygiene is the best way to prevent the need for a root canal. Brush and floss daily to keep your teeth and gums healthy, and visit your dentist regularly for checkups and cleanings. Avoiding habits that can damage your teeth, such as chewing on hard objects, can also help protect your teeth from infections that may require a root canal.